Synchrotron radiation single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy were used to analyze natural ammonium chloride (NH
4Cl) under high pressure. The results show that NH
4Cl transforms from phase IV (space group
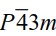
) to phase V (space group
P4/
nmm) at 13.6 GPa. The parameters of the third-order Birch-Murnaghan equation of state are determined with
K0=24.9(1) GPa,
V0=56.4(1) Å
3,
K0′=5.5 for phase IV, and
K0=35(25) GPa,
V0=110(11) Å
3,
K0′=3.8(13) for phase V. The Raman spectrum of NH
4Cl shows new peaks and discontinuity at 13.7 GPa, and the Raman shift are linearly related to pressure. d
νi/d
P and Grüneissen parameters for each vibration of phase IV and V are obtained. The infrared spectrum of N—H vibration split at 11.7–14.8 GPa. The transition pressures from phase IV to V of NH
4Cl, NH
4Br and NH
4I decrease in turn, which are inversely proportional to the anion radius.
在高压环境下, 对天然卤砂(NH
4Cl)进行同步辐射单晶X射线衍射(XRD)、拉曼光谱和红外光谱分析。结果表明, NH
4Cl在13.6 GPa 发生相变, 从IV相(空间群为
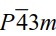
)变为V相(空间群为
P4/
nmm); IV相和V相NH
4Cl的三阶Birch-Murnaghan状态方程参数分别为
K0=24.9(1) GPa,
V0=56.4(1) Å
3,
K0′=5.5以及
K0=35(25) GPa,
V0=110(11) Å
3,
K0′=3.8(13)。NH
4Cl的拉曼光谱在13.7 GPa出现新峰和不连续变化, 其拉曼位移与压强呈现线性关系, 据此获得IV相和V相NH
4Cl各拉曼振动的位移量随压强的变化, 并计算格林乃森参数。NH
4Cl的红外光谱在11.7~14.8 GPa出现N—H振动峰分裂。NH
4Cl, NH
4Br和NH
4I的IV-V相变压强依次降低, 表现出与阴离子半径成反比的规律。
