

Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis ›› 2017, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 639-651.DOI: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2016.127
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yijia ZHENG1,2, Shuhua LIU1( ), Ping HE3(
), Ping HE3( ), Yucong MIAO4, Shu WANG5
), Yucong MIAO4, Shu WANG5
Received:2016-03-08
Revised:2016-06-04
Online:2017-07-20
Published:2017-07-20
郑亦佳1,2, 刘树华1( ), 何萍3(
), 何萍3( ), 缪育聪4, 王姝5
), 缪育聪4, 王姝5
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yijia ZHENG, Shuhua LIU, Ping HE, Yucong MIAO, Shu WANG. Numerical Study of Summertime Urban Heat Island in Dianzhong[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2017, 53(4): 639-651.
郑亦佳, 刘树华, 何萍, 缪育聪, 王姝. 滇中地区夏季城市热岛效应的数值模拟研究[J]. 北京大学学报自然科学版, 2017, 53(4): 639-651.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xbna.pku.edu.cn/EN/10.13209/j.0479-8023.2016.127
| 模式参数 | 参数设置 |
|---|---|
| 模拟时间 | 2010?08?09 06:00至2010?08?11 24:00 |
| 水平分辨率 | 27, 4.5, 1.5 km |
| 水平格点数 | 150×130, 201×201, 202×151 |
| 土地利用类型数据 | MODIS |
| 微物理参数化方案 | Thompson graupel方案 |
| 辐射参数化方案 | RRTMG方案 |
| 积云对流参数化方案 | Kain-Fritsch方案 |
| 边界层参数化方案 | YSU方案 |
| 陆面过程参数化方案 | Noah耦合UCM城市冠层陆面方案 |
Table 1 Run-time, domain configurations and physics options used in the WRF simulation
| 模式参数 | 参数设置 |
|---|---|
| 模拟时间 | 2010?08?09 06:00至2010?08?11 24:00 |
| 水平分辨率 | 27, 4.5, 1.5 km |
| 水平格点数 | 150×130, 201×201, 202×151 |
| 土地利用类型数据 | MODIS |
| 微物理参数化方案 | Thompson graupel方案 |
| 辐射参数化方案 | RRTMG方案 |
| 积云对流参数化方案 | Kain-Fritsch方案 |
| 边界层参数化方案 | YSU方案 |
| 陆面过程参数化方案 | Noah耦合UCM城市冠层陆面方案 |
| 模拟试验 | 土地利用类型 |
|---|---|
| CTL | 采用默认的MODIS地表利用类型数据 |
| Nourb | 将CTL试验中的城市下垫面改为农田 |
| Urban | 将CTL试验中的城市周边的农田改为城市 |
| Nolake | 将CTL试验中的湖泊改为农田 |
Table 2 Landuse in different WRF model simulation
| 模拟试验 | 土地利用类型 |
|---|---|
| CTL | 采用默认的MODIS地表利用类型数据 |
| Nourb | 将CTL试验中的城市下垫面改为农田 |
| Urban | 将CTL试验中的城市周边的农田改为城市 |
| Nolake | 将CTL试验中的湖泊改为农田 |
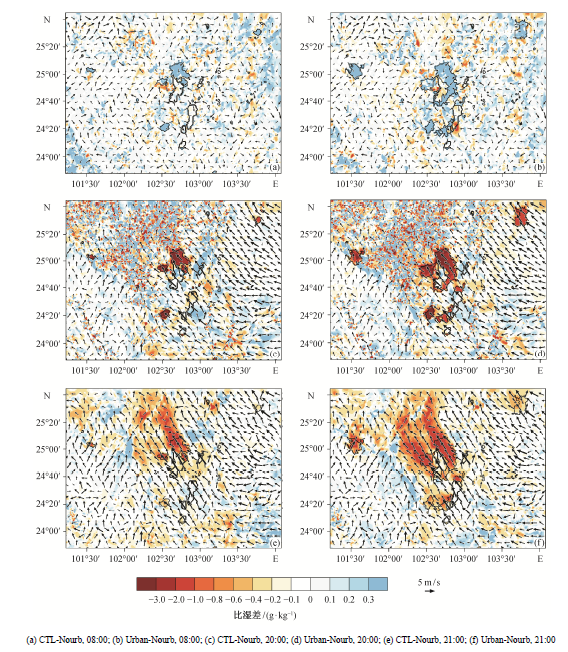
Fig. 5 Distributions of the differences in 2 m specific humidity superposed on 10 m wind vectors rom CTL run at 08:00, 20:00 and 21:00 LST on August 11
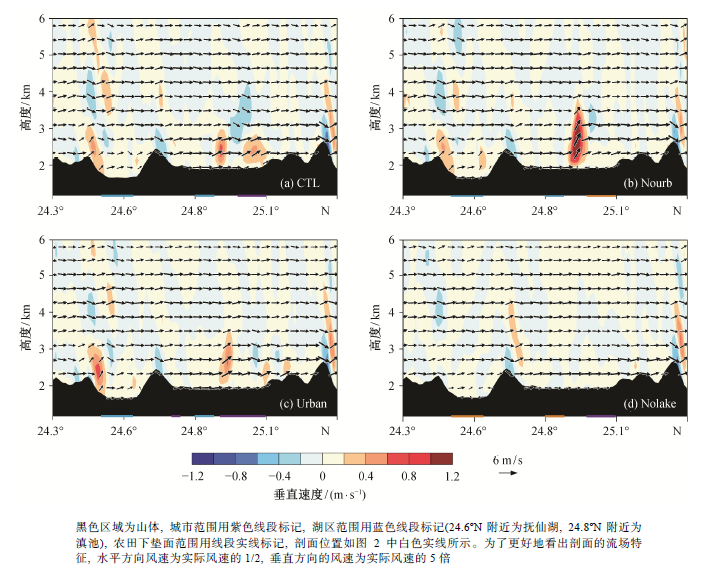
Fig. 7 Distribution of vertical speed and wind vector in the southeast-northwest cross section simulated by different experiments at 03:00 LST on August 10
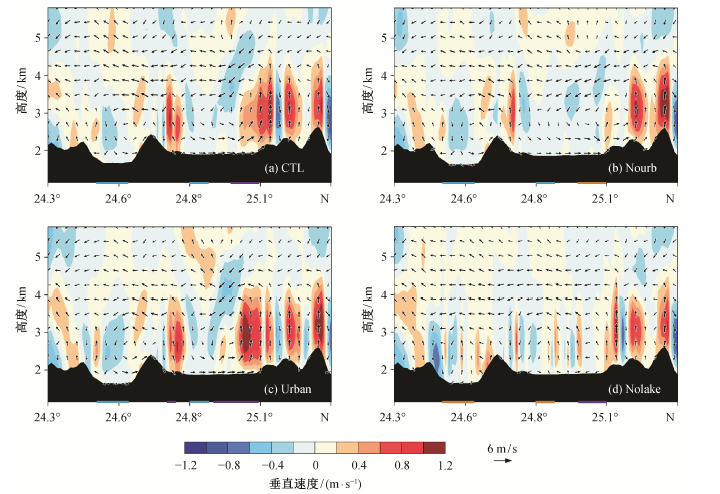
Fig. 8 Distribution of vertical speed and wind vector in the southeast-northwest cross ection simulated by different experiments at 16:00 LST on August 11
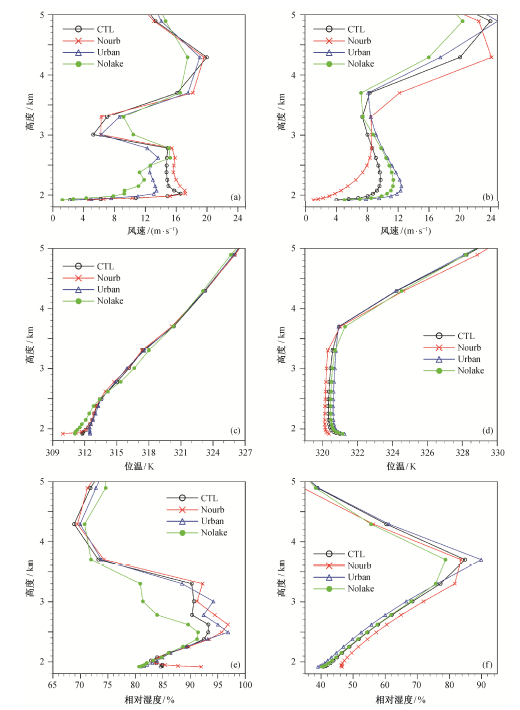
Fig. 9 Vertical profile of wind speed, potential temperature and relative humidity simulated by different experiments at 03:00 LST August 10 ((a), (c) and (e)) and 16:00 LST on August 11 ((b), (d) and (f))) on grid located at 102.79°E, 24.92°N
| [1] | Howard L.The climate of London:deduced from meteorological observations made in the metropolis and at various places around it. Charleston: Nabu Press, 1833 |
| [2] | Manley G.On the frequency of snowfall in metro-politan England. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Me-teorological Society, 1958,84:70‒72 |
| [3] | 寿亦萱, 张大林. 城市热岛效应的研究进展与展望. 气象学报, 2012,70(3):338-353 |
| [4] | Oke T R.City size and the urban heat island. Atmospheric Environment, 1973,7(8):769-779 |
| [5] | Oke T R.The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological So-ciety, 1982,108:1-24 |
| [6] | Morris C J G, Simmonds I, Plummer N.Quanti-fication of the influences of wind and cloud on the nocturnal urban heat island of a large city. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2001,40(2):169-182 |
| [7] | Unger J, Sümeghy Z, Zoboki J.Temperature cross-section features in an urban area. Atmospheric Re-search, 2001,58(2):117-127 |
| [8] | Morris C J G, Simmonds I. Associations between varying magnitudes of the urban heat island and the synoptic climatology in Melbourne, Australia. Inter-national Journal of Climatology, 2000, 20(15): 1931‒ 1954 |
| [9] | 季崇萍, 刘伟东, 轩春怡. 北京城市化进程对城市热岛的影响研究. 地球物理学报, 2006,49(1):69-77 |
| [10] | Adebayo Y R.A note on the effect of urbanization on temperature in Ibadan. Journal of Climatology, 1987,7(2):185-192 |
| [11] | Tereshchenko I E, Filonov A E. Air temperature fluctuations in Guadalajara,Mexico,from 1926 to 1994 in relation to urban growth. International Journal of Climatology, 2001,21(8):1803-1816 |
| [12] | Yang P, Ren G, Liu W.Spatial and temporal charac-teristics of Beijing urban heat island intensity. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2013,52 (8):1803-1816 |
| [13] | Ohashi Y, Kida H.Local circulations developed in the vicinity of both coastal and inland urban areas: a numerical study with a mesoscale atmospheric model. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2002,41(1):30-45 |
| [14] | 刘振鑫, 刘树华, 胡非, 等. MM5和WRF对北京地区低层大气局地环流模拟能力的对比研究. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012,42(2):301-312 |
| [15] | 刘振鑫. 应用城市冠层模式与WRF模式耦合研究城市化效应[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2013 |
| [16] | Miao Y C, Liu S H, Zheng Y J, et al. Numerical study the effects of topography and urbanization on the local atmospheric circulations over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Advances in Meteorology, 2015,Article ID: 397070 |
| [17] | Zhang D L, Shou Y X, Dickerson R R.Upstream urbanization exacerbates urban heat island effects. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009,36(24):88-113 |
| [18] | Zhang D L, Shou Y X, Dickerson R R, et al.Impact of upstream urbanization on the urban heat island effects along the Washington-Baltimore Corridor. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2011,50(10):2012-2029 |
| [19] | 李耀锟, 巢纪平, 匡贡献. 城市热岛效应和气溶胶浓度的动力学、热力学分析. 地球物理学报, 2015,58(3):729-740 |
| [20] | 桑建国. 城市热岛效应的分析解. 气象学报, 1986,44(2):251-255 |
| [21] | 桑建国, 张治坤, 张伯寅. 热岛环流的动力学分析. 气象学报, 2000,58(3):321-327 |
| [22] | 刘树华, 李洁. 城市及乡村大气边界层结构的数值模拟. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002,38(1):90-97 |
| [23] | 胡小明, 刘树华, 梁福明, 等. 北京区域近地边界层特征数值模拟. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005,41(4):514-522 |
| [24] | Miao S, Chen F, LeMone M A, et al. An observational and modeling study of characteristics of urban heat island and boundary layer structures in Beijing.Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2009,48(3):484-501 |
| [25] | 刘树华, 刘振鑫, 李炬. 京津冀地区大气局地环流耦合效应的数值模拟. 中国科学: D 辑, 2009,39(1):88-98 |
| [26] | 刘树华, 刘振鑫, 郑辉, 等. 多尺度大气边界层与陆面物理过程模式的研究进展. 中国科学: G 辑, 2013,43(10):1332-1355 |
| [27] | Zhang N, Chen Y.A case study of the upwind urbanization influence on the urban heat island effects along the Suzhou-Wuxi Corridor. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2014,53:333-345 |
| [28] | Zhao W J, Zhang N, Sun J N, et al. Evaluation and parameter-sensitivity study of a single-layer urban canopy model(SLUCM) with measurments in Nan-jing,China. Journal of Hudrometeorology, 2014,15:1078-1090 |
| [29] | 何云玲, 张一平, 刘玉洪, 等. 昆明城市气候水平空间分布特征. 地理科学, 2002,22(6):724-729 |
| [30] | 赵庆由, 明庆忠. 近20年来昆明市城市化进程对城市热岛效应的影响研究. 云南地理环境研究, 2010,22(4):87-92 |
| [31] | 孙绩华, 冯健武, 段玮. 昆明城市热岛效应变化特征研究. 气候与环境研究, 2015,20(6):645-653 |
| [32] | 何萍, 李宏波, 黄惠. 1960—2009年云南高原楚雄市气候年代际变化特征及城市气候分析. 地理科学进展, 2011,30(1):65-72 |
| [33] | Broxton P D, Zeng X, Sulla-Menashe D, et al. A global land cover climatology using MODIS data.Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2014,53(6):1593-1605 |
| [34] | Thompson G, Field P R, Rasmussen R M, et al. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme.Part Ⅱ: imple-mentation of a new snow parameterization. Monthly Weather Review, 2008,136(12):5095-5115 |
| [35] | Iacono M J, Delamere J S, Mlawer E J, et al. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: calculations with the AER radiative transfer models.Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2008,113(D13):1395-1400 |
| [36] | Chen F, Dudhia J. Coupling an advanced land surface-hydrology model with the Penn State-NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part Ⅰ: model implementation and sensitivity.Monthly Weather Review, 2001,129(4):569-585 |
| [37] | Kusaka H, Kondo H, Kikegawa Y, et al. A simple single-layer urban canopy model for atmospheric models: comparison with multi-layer and slab models. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2001,101(3):329-358 |
| [38] | Kusaka H, Kimura F.Coupling a single-layer urban canopy model with a simple atmospheric model: impact on urban heat island simulation for an idealized case. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan: SerⅡ, 2004,82(1):67-80 |
| [39] | Kain J S.The Kain-Fritsch convective parameteri-zation: an update. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2004,43(1):170-181 |
| [40] | Hong S Y, Pan H L.Nonlocal boundary layer vertical diffusion in a medium-range forecast model. Monthly weather review, 1996,124(10):2322-2339 |
| [41] | Hong S Y, Dudhia J, Chen S H.A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameteri-zation of clouds and precipitation.Monthly Weather Review, 2004,132(1):103-120 |
| [42] | Mass C F, Ovens D. WRF model physics: prob- lems, solutions and a new paradigm for progress. Preprints, WRF Users’ Workshop, Boulder, CO, NCAR [EB/OL]. (2010) [2014‒04‒17]. |
| [43] | Mass C F, Ovens D.Fixing WRF’s high speed wind bias: a new subgrid scale drag parameterization and the role of detailed verification // 24th Conference on Weather and Forecasting/20th Conference on Nume-rical Weather Prediction. Seattle: Amer Meteor Soc B, 2011 [EB/OL]. (2011‒01‒26) [2014‒04‒17]. |
| [44] | 杨建博, 刘红年, 费松, 等. 太湖湖陆风背景下的苏州城市化对城市热岛特征的影响. 气象科学, 2013,33(5):473-484 |
| [45] | Dutra E, Stepanenko V M, Balsamo G, et al.An offline study of the impact of lakes on the perfor-mance of the ECMWF surface scheme. Helsinski: Finnish Environment Insitute, 2010 |
| [46] | Sills D M L, Brook J R, Levy I, et al. Lake breeze in the southern Great Lakes region and their influence during BAQS-Met 2007. Atmospheric Chemisrty and Physics , 2011,11(15): 7955-7973 |
| [1] | LIU Yan, LI Qi, YANG Liu, ZHANG Tengyue, LIU Jiaping. Investigation on Urban Heat Island Intensity Model of the Residential District in Mid & High-Density Cities [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2022, 58(6): 1077-1090. |
| [2] | Yijia ZHENG, Shuhua LIU, Ping HE, Yucong MIAO, Shu WANG. Numerical Simulation of Impact of Urbanization on a Precipitation Process: A Case Study of Heavy Rainfall in Kunming [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2017, 53(4): 627-638. |
| [3] | Yijia ZHENG, Yucong MIAO, Shuhua LIU, Ping HE, Shu WANG. Analysis of Meteorological Variables in Dianzhong Region in Recent 51 Years [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2017, 53(1): 8-18. |
| [4] | CHEN Binhui, FENG Yao, YUAN Jianguo, ZHOU Yimin, ZHAO Xinyi. Spatiotemporal Difference of Urban Heat Island in Jing-Jin-Ji Area Based on MODIS Land Surface Temperature [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2016, 52(6): 1134-1140. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhenzhou,CAI Xuhui,SONG Yu,KANG Ling,HUANG Xin,LI Qinyi. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height over Hainan Island and Its Adjacent Sea Areas [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2013, 49(5): 783-790. |
| [6] | LIU Shuhua,ZHOU Bin. Simulation of Wind, Temperature and Humidity Fields over Beijing Area in Summer Using an Improved Model [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2007, 43(1): 42-47. |
| [7] | HU Xiaoming,LIU Shuhua,LIANG Fuming,WANG Jianhua,LIU Heping,LI Ju,WANG Yingchun. Numerical Simulation of Features of Surface Boundary-Layer over Beijing Area [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2005, 41(4): 514-522. |
| [8] | HU Xiaoming,LIU Shuhua,LIANG Fuming,WANG Jianhua,LIU Heping,WANG Yingchun,LI Ju. Observational Study of Wind Fields, Temperature Fields over Beijing Area in Summer and Winter [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2005, 41(3): 399-407. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||